Architecture
This section presents the static structure of the system using C4 model diagrams. Each level provides increasing detail about the software architecture.
Level 1: System Context
This view shows the Hiero DID SDK JS as a system in its environment and the key actors and external systems it collaborates with. It follows the C4 Model "Context" level.
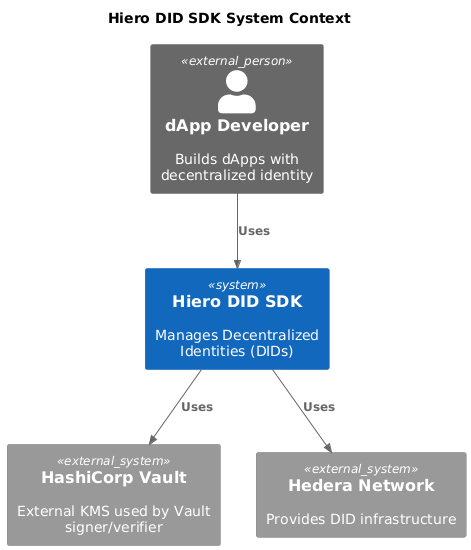
People
-
dApp Developer: Builds dApps with decentralized identity.
-
Operator/DevOps: Configures network access, credentials, and optional external KMS (e.g., HashiCorp Vault).
Software Systems
-
Hiero DID SDK JS (System): Monorepo of npm packages that expose APIs to manage and resolve DIDs on Hedera, plus utilities for cryptography, caching, compression, messaging, and AnonCreds registry integration.
-
Hedera Network (External System): Provides Hedera Consensus Service (HCS) topics, Nodes for submitting transactions, and Mirror Nodes for reading messages.
-
HashiCorp Vault (External System, optional): External KMS used by optional signer/verifier packages for key custody.
Relationships
-
dApp Developer → Hiero DID SDK JS: Calls Registrar to perform DID operations; calls Resolver to resolve DID Documents; may call AnonCreds registry APIs.
-
Hiero DID SDK JS → Hedera Network: Publishes DID operations to HCS topics via Hedera Clients; reads topic messages via Mirror Node APIs.
-
Hiero DID SDK JS → HashiCorp Vault (optional): Uses Vault-backed signer/verifier packages for signing and verification without exposing private keys.
Level 2: Container View
This view identifies the main containers (runnable units and libraries) inside the Hiero DID SDK JS and their relationships with external systems. It follows the C4 Model "Container" level.
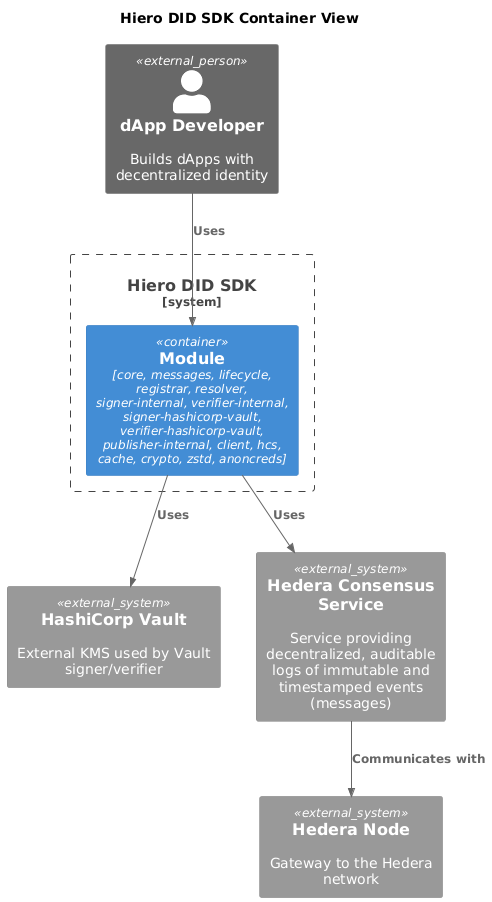
Internal Containers (npm packages)
-
core: Common types, interfaces, and utilities shared by all packages.
-
messages: DID message formats and lifecycle events.
-
lifecycle: Async orchestration utilities for DID flows.
-
registrar: High-level API to create/update/deactivate DIDs. Depends on messages, signer, publisher, hcs, client.
-
resolver: High-level API to resolve DIDs from Hedera. Depends on hcs topic reader, cache, verifier, client.
-
signer-internal: Local signing using Hedera PrivateKey.
-
verifier-internal: Local verification of signatures.
-
signer-hashicorp-vault (optional): Vault-backed signing.
-
verifier-hashicorp-vault (optional): Vault-backed verification.
-
publisher-internal: Publishes transactions to Hedera via Client.
-
client: Configures and provides Hedera SDK Client per network.
-
hcs: Abstraction over Hedera Consensus Service (publish/read topics, publish/read messages, submit/resolve files by HCS-1 standard).
-
cache: In-memory cache primitives used by resolver and others.
-
crypto: Cryptographic helpers (SHA-256 hashing).
-
zstd: Compression utilities used to reduce on-chain payload size.
-
anoncreds: Hedera AnonCreds Registry implementation per spec.
External Containers
-
Hedera Nodes: Submit transactions (DID ops) to the network.
-
Hedera Mirror Node: Read topic info and messages for resolution.
-
HashiCorp Vault (optional): External KMS used by Vault signer/verifier.
Relationships
-
registrar → signer(-internal | -vault): to sign DID operations.
-
registrar → publisher-internal → client → Hedera Nodes: to submit HCS transactions.
-
resolver → hcs (Topic Reader) → Mirror Node: to fetch topic messages; may use cache and zstd for performance.
-
resolver → verifier(-internal | -vault): to verify signatures of DID messages/documents.
-
hcs → client: to publish to HCS topics.
-
anoncreds → hcs/client: to interact with Hedera AnonCreds registry.
Notes
Each container is versioned and published independently, enabling consumers to choose only what they need. See Packages Guide for details and links.
Level 3: Component View
This diagram provides a detailed view of the components within the Hiero DID SDK and their interactions with each other and with external dependencies. It illustrates the internal workings of the SDK and how it facilitates DID management.
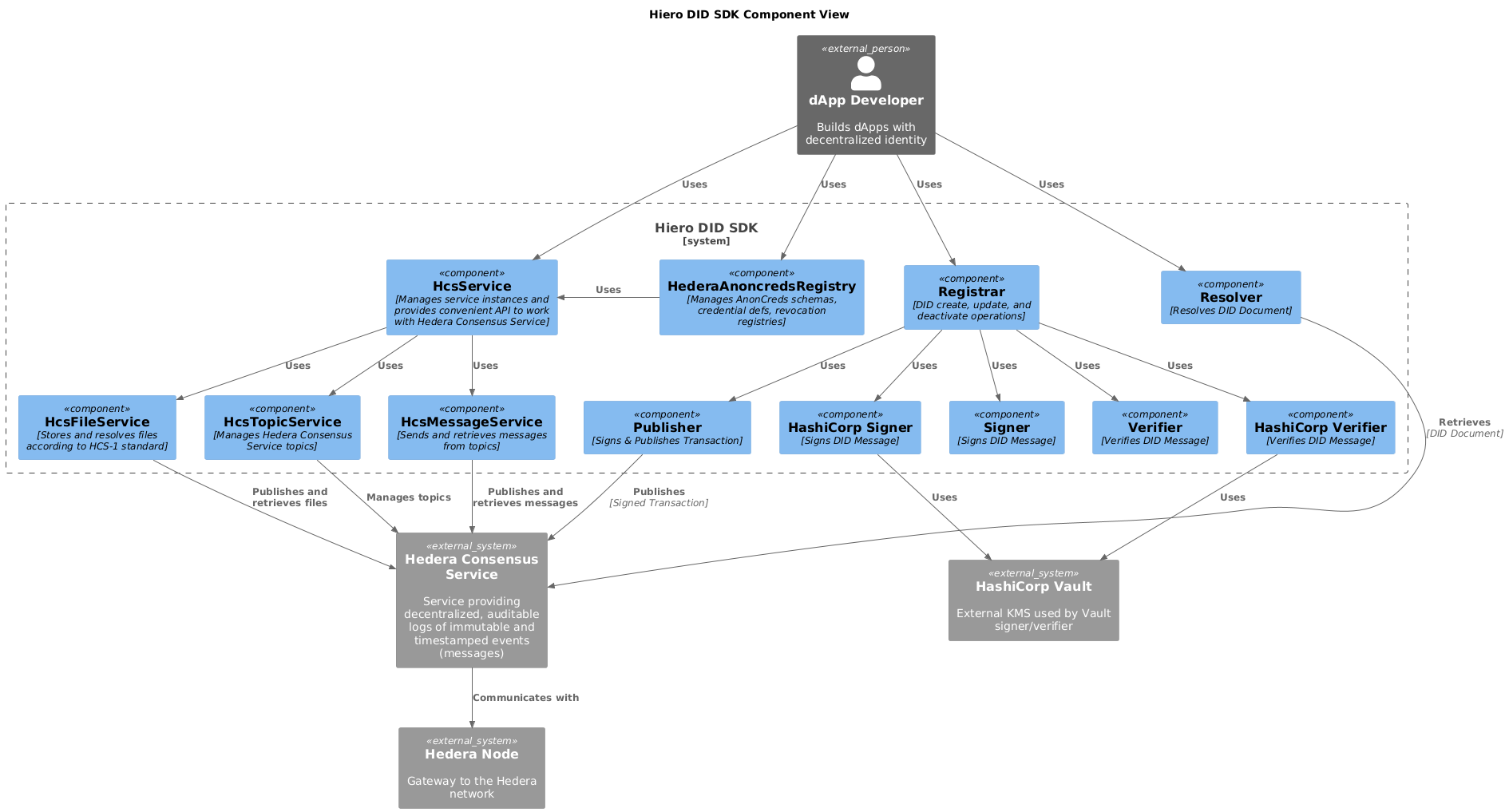
Components
-
dApp Developer: Builds dApps with decentralized identity.
-
Hiero DID SDK: The software development kit comprising the following components and services:
-
Registrar: Handles creation, updating, and deactivation of DIDs.
-
Resolver: Resolves DIDs to their corresponding DID Documents.
-
HcsService: Central service managing Hedera Consensus Service (HCS) objects; responsible for initializing the Hedera client and cache.
-
HederaAnoncredsRegistry: Manages registration and resolution of AnonCreds schemas, credential definitions, revocation registries, and revocation status lists on Hedera.
-
Signer: Signs DID messages to ensure cryptographic integrity.
-
Verifier: Verifies DID messages using internal cryptographic.
-
HashiCorpSigner: Signs DID messages using HashiCorp Vault.
-
HashiCorpVerifier: Verifies DID messages using HashiCorp Vault.
-
Publisher: Signs and publishes transactions to the Hedera Topic Service.
-
HederaClientService: Manages Hedera SDK clients for multiple networks, handling client lifecycle and configuration.
-
HcsTopicService: Manages creation, update, deletion, and retrieval of topics within the Hedera Consensus Service.
-
HcsMessageService: Handles sending and retrieving messages from HCS topics.
-
HcsFileService: Provides file storage and retrieval capabilities using the HCS-1 standard, with automatic Zstandard compression and integrity verification.
-
Cache Service: Caches data and query results to improve performance and reduce redundant network requests.
-
Crypto Library: Provides cryptographic functions such as SHA-256 hashing.
-
Zstd Compression: Module for compressing and decompressing data using the Zstandard algorithm.
External Systems
-
Hedera Consensus Service: Hedera’s publish/subscribe messaging platform through which DID topics and messages are exchanged.
-
Hedera Node: Hedera network node that acts as a gateway for submitting transactions and interacting with the blockchain.
Interactions
-
dApp Developers use Registrar, Resolver, HcsService, and HederaAnoncredsRegistry: Developers interact with these components to manage decentralized identifiers, resolve DID documents, manipulate HCS objects, and register AnonCreds data.
-
Registrar uses Signer and Publisher: Registrar signs DID-related messages with the Signer and publishes these signed transactions to the Hedera network via the Publisher.
-
Publisher publishes signed transactions to the Hedera Consensus Service: Publisher submits signed transactions as messages to HCS topics.
-
Resolver retrieves DID Documents from the Hedera Consensus Service: Resolver queries DID document data by reading messages from HCS topics.
-
HcsService initializes HederaClientService and Cache Service: HcsService sets up the network client and caching mechanism for HCS operations.
-
HcsService uses HcsTopicService, HcsMessageService, and HcsFileService: Delegates topic, messaging, and file operations to specialized services.
-
HcsTopicService, HcsMessageService, HcsFileService use HederaClientService: These services leverage the Hedera SDK client for network interactions.
-
HcsTopicService, HcsMessageService, HcsFileService use Cache Service: All these services utilize caching to enhance data retrieval efficiency.
-
HcsFileService uses Crypto Library and Zstd Compression: For file compression during storage and retrieval.
-
HcsMessageService publishes and retrieves messages from Hedera Consensus Service: Manages message sending and receiving through topics.
-
HcsFileService publishes and retrieves files from Hedera Consensus Service: Manages chunked file submissions and retrieval with compression.
-
HcsTopicService manages topics in the Hedera Consensus Service: Oversees topic lifecycle (creation, update, deletion).
-
HederaAnoncredsRegistry uses HcsService: Uses HCS services to store and retrieve AnonCreds-related data on Hedera.
-
Hedera Consensus Service communicates with Hedera Node: The underlying infrastructure supporting message publication and retrieval.
Level 4: Runtime View
This diagram illustrates the runtime interactions between the components of the Hiero DID SDK, a dApp developer, and the Hedera network during a typical DID management workflow. It shows the sequence of operations and how data flows between the components.
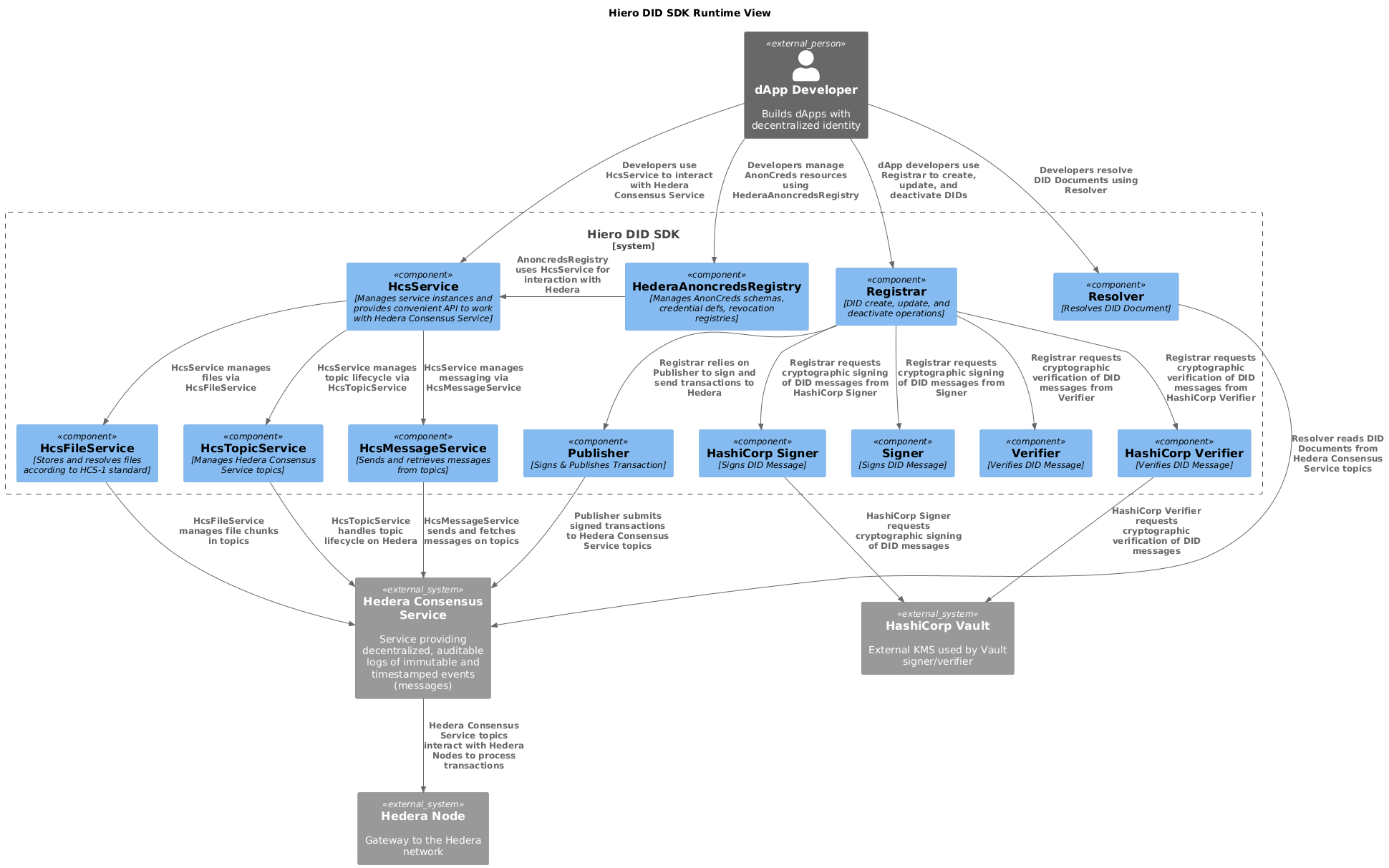
Components
-
dApp Developer: Builds dApps with decentralized identity.
-
Hiero DID SDK: The software development kit providing key components to work with decentralized identity on Hiero:
-
Registrar: Handles creation, update, deactivation, and resolution of DIDs at runtime.
-
Resolver: Resolves DID Documents upon developer’s request.
-
Signer: Signs DID messages and transactions to ensure integrity and authenticity.
-
Publisher: Signs and publishes transactions to the Hedera Consensus Service (HCS).
-
HcsService: Coordinates Hedera Consensus Service objects handling and initializes underlying services.
-
HcsTopicService: Manages HCS topics lifecycle (create, update, delete) used for DID communication.
-
HcsMessageService: Sends messages to and retrieves messages from HCS topics.
-
HcsFileService: Handles chunked file submission and retrieval with compression and verification.
-
HederaClientService: Provides configured Hedera SDK clients for interacting with Hedera networks.
-
Cache Service: Caches frequently used data to enhance performance.
-
Crypto Library: Provides cryptographic utilities (e.g., SHA-256 hashing).
-
Zstd Compression: Offers compression and decompression using the Zstandard algorithm.
-
HederaAnoncredsRegistry: Manages decentralized anonymous credentials (AnonCreds) data lifecycle on Hedera.
-
Hedera Consensus Service: The Hedera network service providing publish/subscribe messaging on topics.
-
Hedera Node: The blockchain node gateway handling transaction submission and state queries.
Runtime Workflow Interactions
-
DID Operation Initiation: The dApp developer triggers a DID operation (create, update, deactivate, or resolve) via the Registrar or Resolver components.
-
Signer Interaction: For operations involving DID messages, the Registrar requests the Signer to cryptographically sign the messages, ensuring authenticity.
-
HCS Object Management: The Registrar invokes HcsService, which orchestrates interactions with HcsTopicService, HcsMessageService, and HcsFileService to handle topic creation, message sending, or file storage.
-
Transaction Preparation and Publishing: The Publisher publishes the signed transactions to the Hedera Consensus Service.
-
Ledger Interaction: The Hedera Consensus Service communicates with one or more Hedera Nodes to persist, order, and propagate the transactions.
-
Caching for Efficiency: The Cache Service caches Hedera Consensus Service data to reduce redundant network calls.
-
Message and File Retrieval: The Resolver, when resolving DID Documents, uses TopicReader for retrieving messages. The HcsFileService, when resolving files, uses HcsTopicService to retrieve chunk messages, builds file payload from them according to HCS-1 standard (decompressing via Zstd Compression and verifying integrity with the Crypto)
-
Hedera Client Usage: All interactions with the Hedera network (making calls, submitting transactions) pass through clients managed by HederaClientService, which handles multi-network configurations and client lifecycle.
-
Anoncreds Data Management: The HederaAnoncredsRegistry uses HcsService and related messaging/file services to register schemas, credential definitions, revocation registries, and status lists, ensuring decentralized credential management atop Hedera.
Data Flow Summary
-
Developer → Registrar/Resolver: Triggers DID management or resolution.
-
Registrar → Signer: Signs DID messages.
-
Registrar → HcsService → (HcsTopicService, HcsMessageService, HcsFileService): Manages Hedera topics, messages, files.
-
Publisher → Hedera Topic Service: Publishes signed transactions.
-
Hedera Topic Service ↔ Hedera Node: Processes transactions and returns state.
-
Resolver → HcsMessageService/HcsFileService → Cache: Retrieves and caches DID documents and credential data.
-
All Ledger interactions → HederaClientService: Provides configured clients for network operations.
-
HederaAnoncredsRegistry ↔ HcsService: Manages AnonCreds lifecycle on ledger.